Introduction
Every year Word Bank release Doing Business report. This report ranks countries on the basis of Distance to Frontier, an absolute score that measures the gap between India and the global best practice. Two India Cities which are scored is Delhi and Mumbai with weight age of 47% and 53% respectively.
Major Highlights related to India
- Absolute score improved from 55.27 to 60.76
- Jumps 30 positions to 100 in World Bank’s ease of doing business ranking
- Among the 10 countries that have improved the most this year.
- Only economy in South Asia to join the list of the 10 top improvers.
- Within South Asia, India has the highest score (80) for protecting minority investors compared
- Ranking on 10 indicators. ( however evaluation on 11)

- However reforms has been done 8 out of 10 parameters but shown improvement in 6 out of 10 parameters in term of ranking

Reform RECOGNIZED by World Bank
Starting a business
- India made starting a business faster
- by merging the applications for the Permanent Account Number (PAN) and the Tax Account Number (TAN)
- by improving the online application system.
- This reform applies to both Delhi and Mumbai.
- Mumbai also made starting a business faster by merging the applications for value added tax and the Profession Tax (PT).
Dealing with construction permits
- implementing an online system that has streamlined the process at the Municipality of New Delhi and Municipality of Greater Mumbai.
- This resulted into Reducing the number of procedures and time required to obtain a building permit by
Getting credit
- Amending the rules on priority of secured creditors outside reorganization proceedings
- Adopted a new law on insolvency that provides a time limit and clear grounds for relief to the automatic stay for secured creditors during reorganization proceedings.
- Strengthened access to credit
Protecting minority investors
- Increasing in remedies available in cases of prejudicial transactions between interested This reform applies to both Delhi and Mumbai.
- Strengthened minority investor
Paying taxes
- India made paying taxes easier by requiring that payments be made electronically to the Employees Provident Fund
- introducing a set of administrative measures easing compliance with corporate income tax.
Trading across borders
- Reduced import border compliance time in Mumbai by improving infrastructure at the Nhava Sheva Port.
- Export and import border compliance costs were also reduced by eliminating merchant overtime fees and through the increased use of electronic and mobile platforms.
Enforcing contracts
- Introduce the National Judicial Data Grid, which makes it possible to generate case management reports on local courts.
- Enforcing contracts become easier
Resolving insolvency
- Adoption of a new insolvency and bankruptcy code that introduced a reorganization procedure for corporate debtors and facilitated continuation of the debtor’s business during insolvency proceedings.
- Resolving insolvency easier
Labor market regulation
- India increased the mandatory length of paid maternity leave. \
reforms which are not acknowledged by the Ease of Doing Business Team (EoDB).
- Reduction in number of procedure (to 8) to get the construction permit
- Simplyfying trading across the borader
- Enforcing Contract:: Maharashtra and Delhi established Commercial Division benches and Commercial Appellate Division benches
- RAPID- Revenue, Accountability, Probity, Information and Digitalization
- for administrating the tax reforms to make tax compliances more taxpayer-friendly, transparent with the aim of widening the tax base.
Had these reforms been taken into the account by EDBT then rank of India in Ease of Doing would be even better than 100.
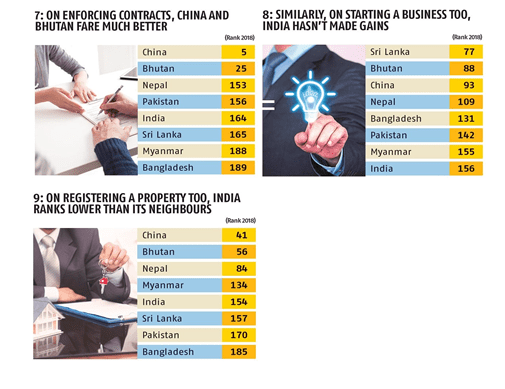
Comparison
India still continues to rank lower than its neighbors Bhutan and China

Other Highlights of Report not particular to India
- Theme: “Reforming to Create Jobs”
- Doing Business 2018 is the 15th in a series of annual reports
- This report investigating the regulations that enhance business activity and those that constrain it.
- Doing Business presents quantitative indicators on business regulation and the protection of property rights that can be compared across 190 economies—from Afghanistan to Zimbabwe—and over time.
- Doing Business measures aspects of regulation affecting 11 areas of the life of a business.
- Ten of these areas are included in this year’s ranking on the ease of doing business. ( listed in above table)
- Doing Business also measures features of labor market regulation, which is not included in this year’s ranking.
- Data in Doing Business 2018 are current as of June 1, 2017. The indicators are used to analyze economic outcomes and identify what reforms of business regulation have worked, where and why.
- South Asia is the only region not represented in the top 50 ranking for ease of doing business.
- Apart from India other 9 countries shown the most notable improvement
- Brunei Darussalam, Thailand, Malawi, Kosovo, Uzbekistan, Zambia, Nigeria, Djibouti and El Salvador.


